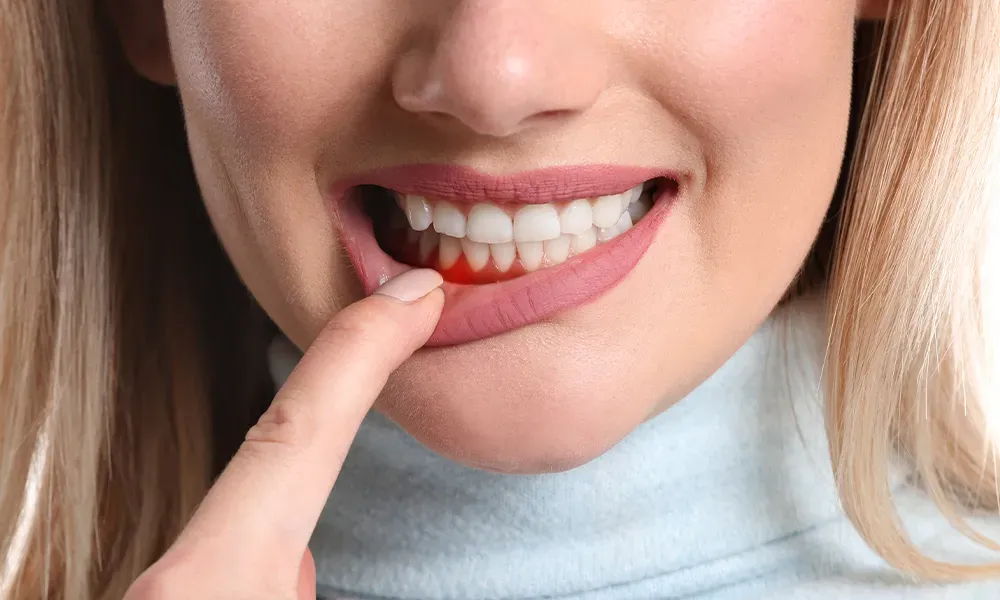

Periodontal disease, also known as periodontitis, is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the gums, bone, and surrounding tissues of the teeth. It is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide, with severe cases leading to tooth loss and even systemic health complications. The dental services in Concord, NC aim at early detection of periodontal disease to pave the way for a discreet treatment plan.
In this article, we will delve into the realm of periodontal disease, exploring its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease is a form of progressive gum disease that is usually caused due to bacterial infiltration. It may begin as a simple gum inflammation (gingivitis), and may gradually progress to affect the supporting tissues of the gums, and the underlying alveolar bone (periodontitis).
How is periodontal disease caused?
Periodontal disease is caused by the accumulation of bacterial plaque on the teeth and gums. If left unchecked, this plaque hardens into calculus, which irritates the gums and triggers an inflammatory response. The bacteria in the plaque produce toxins, and acids that damage the gums, bone, and surrounding tissues, leading to the destruction of the periodontium, namely the gums, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone.
Are there any risk factors for periodontal disease?
Several risk factors contribute to the development of periodontal disease, including:
- Genetic predisposition
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking and other tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Stress
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Medications like antihypertensives, and antidepressants
- Excess alcohol consumption
- Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy and menopause
- Orthodontic braces due to poor teeth cleaning
What are the clinical manifestations of periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease often presents with few clinical features in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, patients may experience:
- Red, swollen, and bleeding gums
- Sore, tender gums
- Bad breath
- Pain while biting or chewing
- Gum recession
- Gaps between teeth
- Loose teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
What are the stages of periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease progresses through several stages, including:
Gingivitis: This is the mildest form of periodontal disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
Periodontitis: This moderate stage of periodontal disease is characterized by the pulling away of gums from the teeth surfaces, forming pockets that harbor bacteria and lead to bone and tissue destruction.
Advanced periodontitis: This is the most severe form of periodontal disease that results in significant bone and tissue loss, and potentially tooth loss.
How do dentists diagnose periodontal disease?
Your dentist will first record your symptoms, and medical history. This helps them determine any genetic predisposition, and rule out the presence of debilitating issues like diabetes. This is followed by diagnosing the condition through a comprehensive dental examination, including:
- Visual examination of the teeth and gums
- Periodontal probing to measure pocket depth
- X-rays to assess bone loss
- Blood testing to identify the presence of periodontal pathogens
How is periodontal disease treated?
Treatment of periodontal disease depends on the severity of the disease and may include:
- Scaling and root planing: A deep cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and gums using specialized ultrasonic instruments. This is followed by teeth polishing to smoothen the surface, thus preventing plaque from adhering to them
- Antibiotics: These medications help combat bacterial infections. Examples include penicillin
- Surgery: Advanced stages of periodontal disease are surgically treated to repair damaged tissues and bone.
- Laser therapy: This is a minimally invasive treatment protocol to reduce pocket depth and promote quick healing with minimal complications.
Can you prevent periodontal disease?
Prevention is key in managing periodontal disease. Strategies include:
- Brushing and flossing regularly
- Regular dental cleanings and check-ups
- Quitting smoking
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Controlling medical conditions like diabetes
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques and counseling
Are there any systemic health complications?
Yes, periodontal disease has been linked to several systemic health complications, including:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Respiratory disease
- Osteoporosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Bottom line
Periodontal disease is a prevalent and destructive condition that affects millions of people globally. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial in managing this disease. By maintaining good oral hygiene, visiting the dentist regularly, and managing risk factors, individuals can reduce their risk of developing periodontal disease and its associated systemic health complications.


